Hemp has a rich and fascinating history, dating back to around 8,000 BCE in ancient Taiwan and China. It has been used for various purposes, such as creating rope, cloth, paper, building materials, and even as animal feed. Additionally, it has been used for medicinal purposes for thousands of years, including for pain relief and sleep.
In the United States, hemp was a major crop for the first 150 years. However, in the 1930s, hemp was grouped with marijuana as the government cracked down on cannabis use. It wasn’t until the 2018 USDA Farm Bill that hemp could be legally grown, processed and sold in the United States. And it wasn’t until the Cannabis Act that same year in Canada, that Canadians could legally produce, obtain and consume CBD & THC products. This legalization led to renewed interest in studying the medical benefits of cannabis, particularly after the discovery of the endocannabinoid system in the early 1990s.
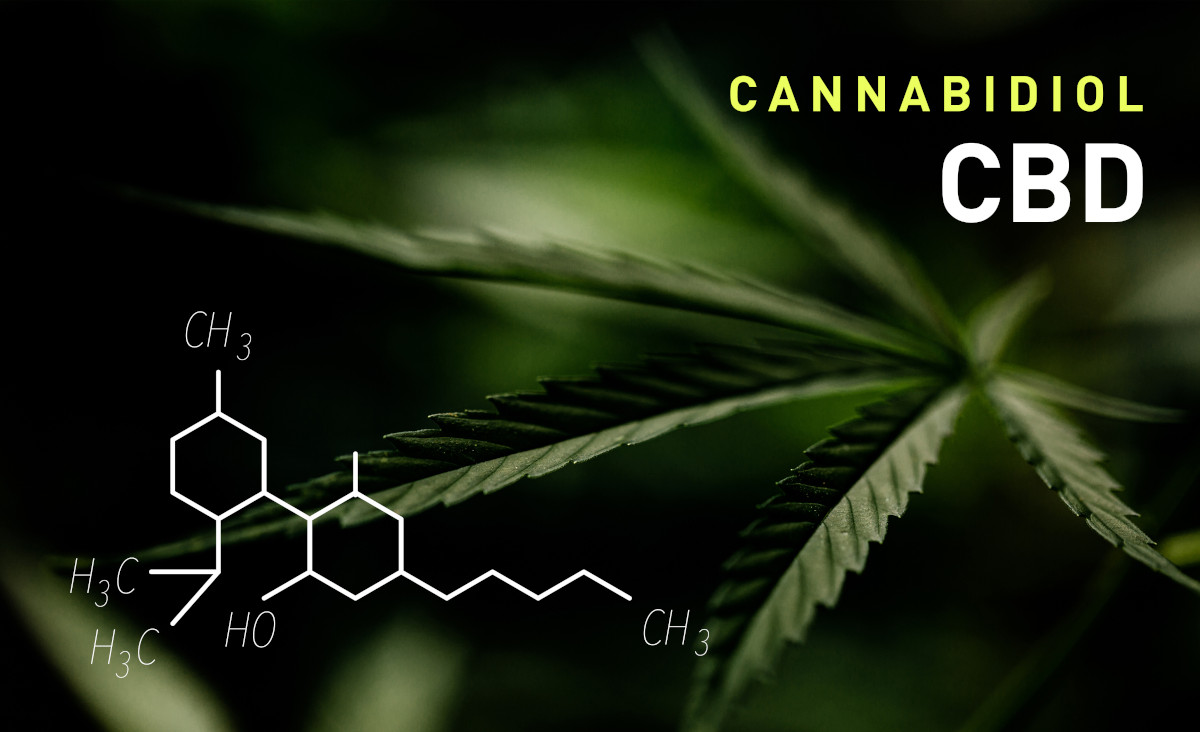
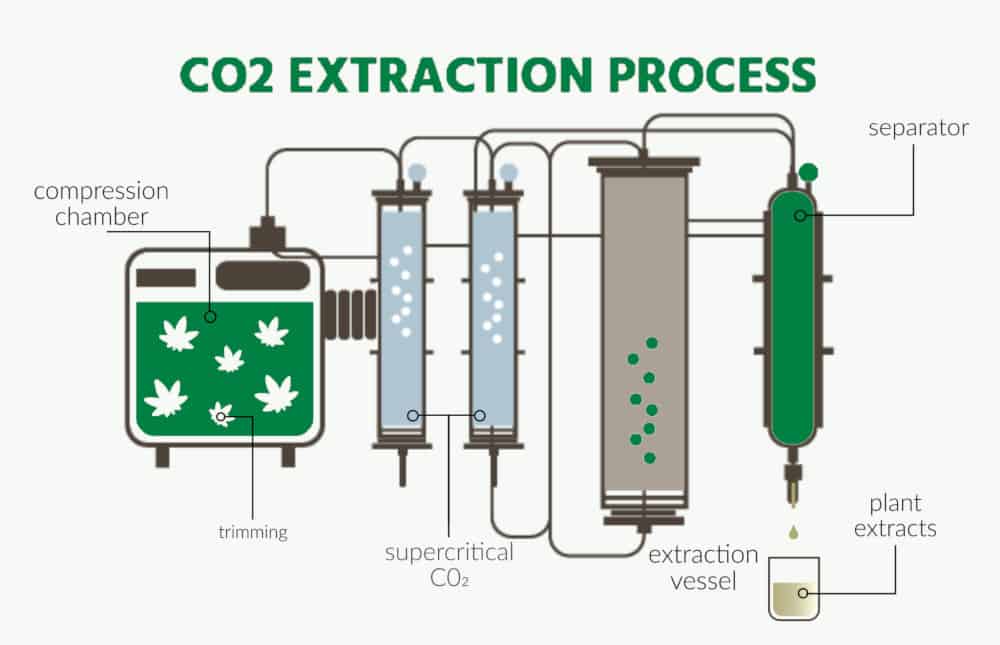
CBD is derived from the hemp plant, but it’s not the only oil that can be derived from the cannabis hemp plant. Hemp seed oil is extracted from the seeds of the plant, but it has different benefits than CBD oil which is extracted from the buds, leaves and stalks. Hemp seed oil is mainly used in beauty and skincare products.
Therefore, when shopping for CBD products, it is important to check the label carefully to ensure you are getting the right product. There’s a possibility of purchasing a beauty product instead of the intended CBD oil.